With IP Cameras
Our IP Cameras shoot in HD at 1080p (2MP), (about
2x 1080P), or
Available in or
body styles
Some models have advanced features like or
The IP Camera Difference: HD, POE, and Networked
An IP camera, or Internet Protocol camera, is a digital video camera that operates on a network. IP cameras are digital and connect via Cat5 (Networking) Cable.
Our IP Cameras can shoot in HD at 1080p, 4MP, and 4K or even greater than 4K.
IP cameras differ from cheaper analog cameras that use siamese cable, aren't HD, and are not digital devices.
Helpful Guides
Accessories
Why IP Cameras are superior to Analog ones
Better Resolution: 1080P to 4K and beyond
IP cameras offer an increased resolution. High-definition (HD) quality recording makes identifying faces and license plates much easier than standard definition.
IP camera technology long ago surpassed previous analog cameras. Their HD recording features reduce the number of cameras needed to properly secure an area. They also allow for recording at a wider angle while still capturing detailed footage that can identify suspects when being presented as courtroom evidence.
Analog

Lowest level HD (1080P)

Easy to use: One cable set up
When you pair our line of Admiral, Admiral Pro POE (Power Over Ethernet), and Imperial NVRs with our SCW IP Cameras, you'll have no trouble installing and configuring your new system.
Simply plug the Cat5e cable into the NVR's POE ports, and the NVR will set up, manage, and power the IP surveillance cameras for you. Setup is so easy we call it “plug & play.”
POE allows a single cable to provide both electric power and data connection to devices such as IP cameras. That means that you run one cable and you're done!
Additionally, the former 300 feet limitations on cable transmission are no more. SCW cameras feature a 750 feet POE Extended Transmission, simplifying system installation.
IP: anyone can do it

Analog: needs an electrician

Video Analytics: Line-crossing, face, and intrusion detection
Video analytics is a series of technologies that automatically analyzes video to detect and determine events not based on a single image but upon the changes in the video stream.
Through VCA (Video Content Analysis), event-recording mode alerts you with intrusion detection precision when an individual enters an area, lingers in an area, or covers, damages, or moves a camera lens. You can also search your video footage for these events.
Even our most basic cameras offer VCA that includes Line-Crossing, Intrusion Detection, and Face Detection that can switch on recording, or trigger Snapshot. The Snapshot feature can automatically upload images to your FTP server (File Transfer Protocol communicates files from server to client on a computer network). Or, Snapshot can send those same images to you as an Email Alert.
PC, Mac, Android, and iOS software is also included free.
Motion Grid

Line crossing

Lingering in an Intrusion Zone

How to Choose the right IP Camera for you
Choosing the Right Resolution: Resolution Matters Most
Nothing impacts identifying a face more than resolution.
When used to describe a digital camera, resolution refers to the size of the digital image the camera produces. It is expressed in terms of how many million pixels it can record in a single image--megapixels.
An IP surveillance camera that captures 1600 x 1200 pixels produces an image with a resolution of 1.92 million pixels as a result of multiplying the vertical and horizontal dimensions (1,600 x 1,200 = 1,920,000). In the industry that is referred to as a 2.0-megapixel (mega here meaning "million") camera (or 2MP or 1080P).
- More resolution means better quality, depending on the camera optics and the quality of the image capture chip
- The advantage of having a camera with a higher resolution is in having more pixels to work with. More pixels means a greater likelihood of identifying an individual
- You can enlarge images (or digitally zoom)-- only to the point of the camera's max resolution--without degrading the quality
Scroll your mouse pointer over this image to see the Digital Zoom for 1080P
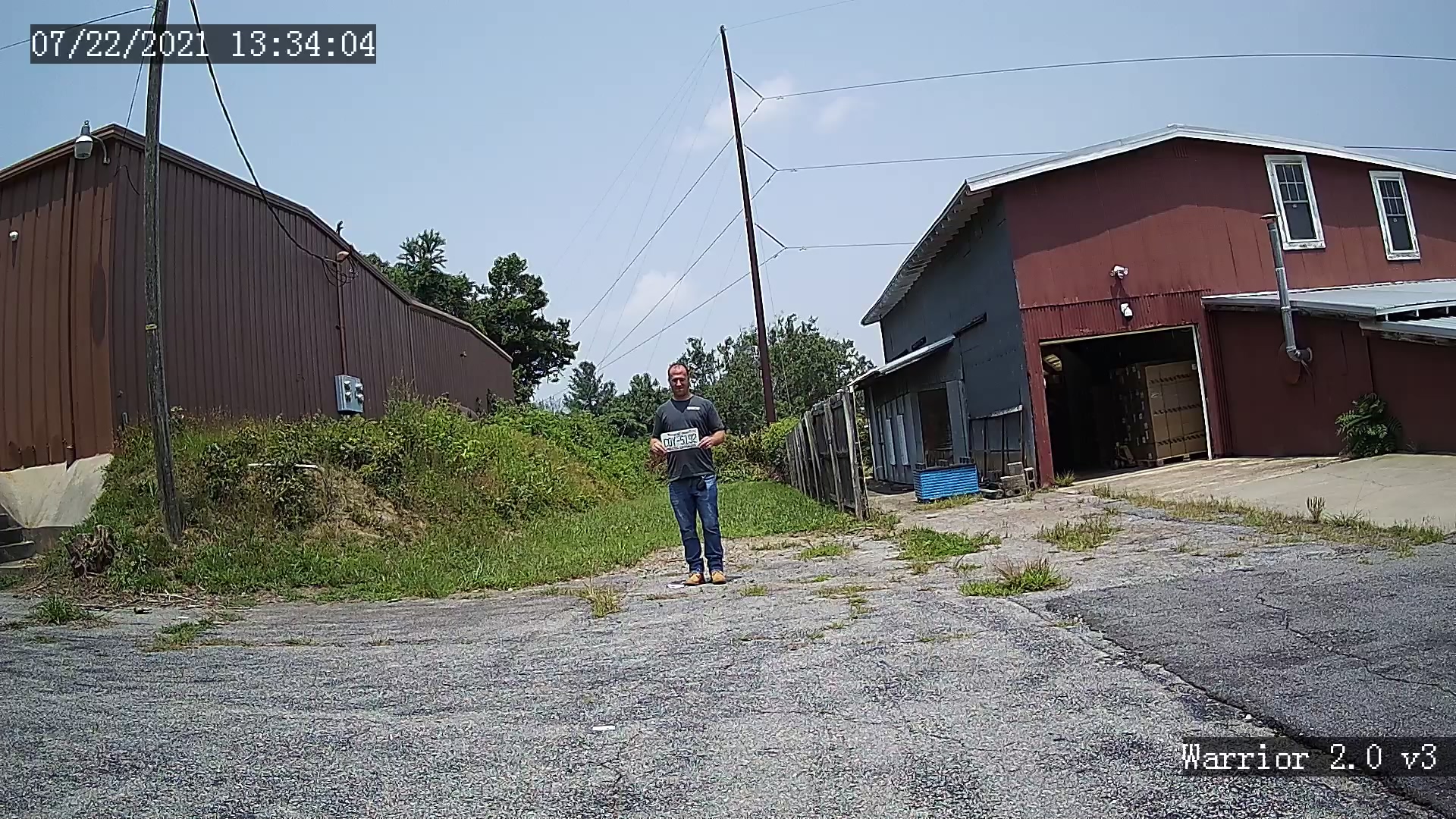

Scroll your mouse pointer over this image to see the Digital Zoom for 4K
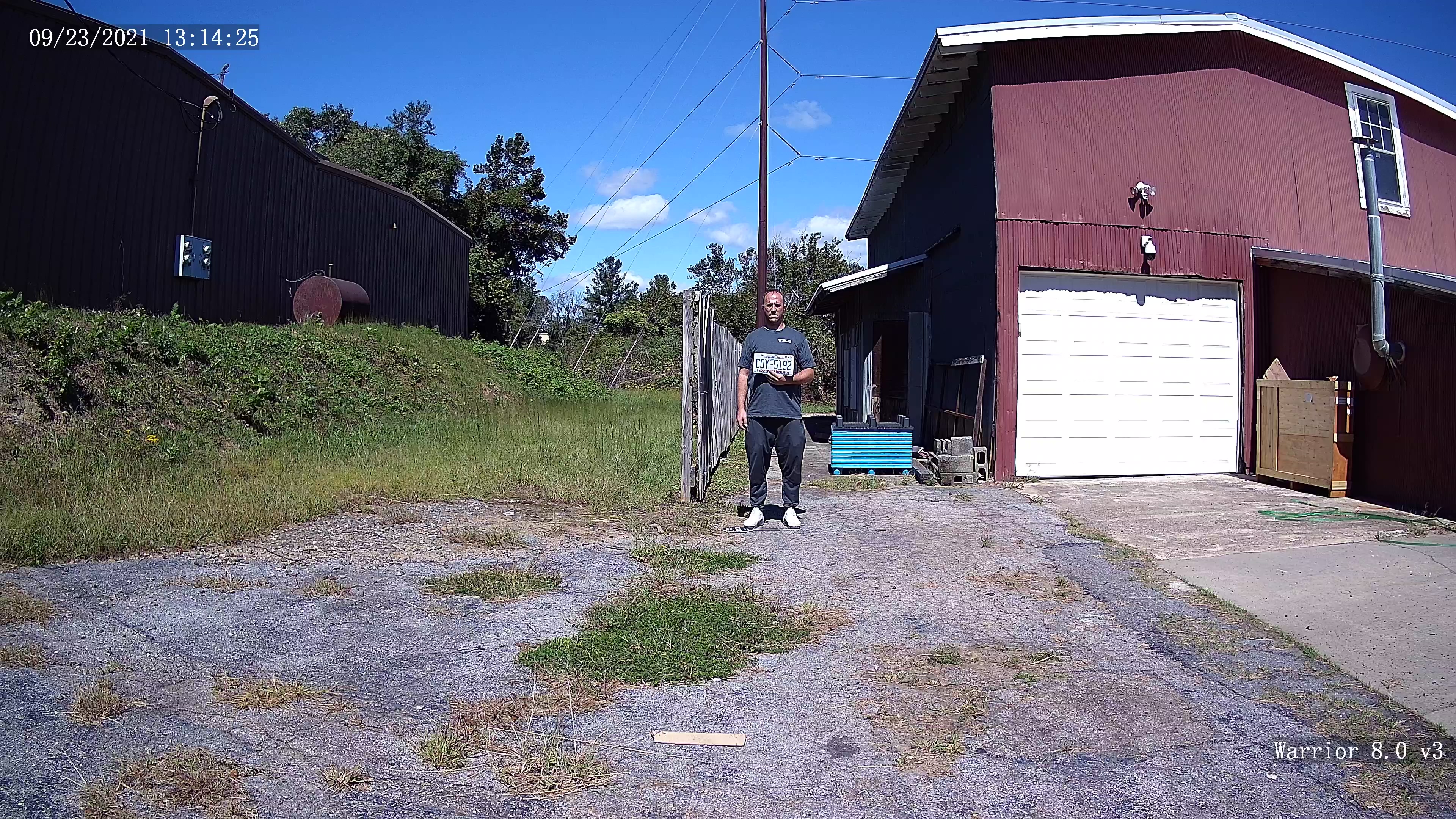

When shopping for IP surveillance cameras, although two different cameras may have the number 4 in the name, note that 4K is double the image quality of a 4MP camera.
1080P is roughly 2 Million Pixels. 4MP stands for 4 Million Pixels. A 4K IP camera captures images at 8,294,400 total pixels, which is a little more than 4x the size of 1080P.
Taking the time to reference and understand these numbers will make a significant impact on matching your expectations with the performance capabilities of the IP cameras you purchase.
Let's compare two similar camera models, the Deputy 2MP at 1080P vs the Deputy 8MP at 4K, to isolate the difference that resolution makes:
As you can see below, the increase in resolution doubles the distances that you can detect, recognize, and identify a person. On all our cameras, we list the real world day-time expectations of the resolution and viewing angle, like so:
The 1080P (2MP) version:
Detect someone up to 75 feet
"Detecting" a face means being able to tell that a human face is in the picture.
Recognize someone up to 40 feet
"Recognizing" a face refers to being able to say "I have seen that person before" - even if you don't know or can't place who it is.
Identify someone up to 20 feet
"Identification" refers to being able to make out identifiable marks with enough certainty to make a sketch or claim.
Same camera with 8MP (4K) resolution
Detect someone up to 150 feet
"Detecting" a face means being able to tell that a human face is in the picture.
Recognize someone up to 85 feet
"Recognizing" a face refers to being able to say "I have seen that person before" - even if you don't know or can't place who it is.
Identify someone up to 45 feet
"Identification" refers to being able to make out identifiable marks with enough certainty to make a sketch or claim.
Choosing the Right IP Camera Lens Type: Fixed, Varifocal, and PTZ
Detect someone up to 75 feet
"Detecting" a face means being able to tell that a human face is in the picture.
Recognize someone up to 40 feet
"Recognizing" a face refers to being able to say "I have seen that person before" - even if you don't know or can't place who it is.
Identify someone up to 20 feet
"Identification" refers to being able to make out identifiable marks with enough certainty to make a sketch or claim.
Detect someone up to 150 feet
"Detecting" a face means being able to tell that a human face is in the picture.
Recognize someone up to 85 feet
"Recognizing" a face refers to being able to say "I have seen that person before" - even if you don't know or can't place who it is.
Identify someone up to 45 feet
"Identification" refers to being able to make out identifiable marks with enough certainty to make a sketch or claim.
Choosing the Right IP Camera Lens Type: Fixed, Varifocal, and PTZ
IP cameras come with one of three lens types:
- Fixed, where the lens cannot move to modify the field of view, focal length, or level of zoom
- Varifocal, where the lens is adjustable to adapt it to different focal lengths, although you have to refocus the camera after adjusting it. Varifocal cameras are either manual or motorized. All SCW varifocal cameras are motorized; this means that you can control the zoom and focus from the camera or NVR--no ladders, no tiny knobs, just simple. easy, controls on a screen.
- PTZ, which is similar to a varifocal lens in that the lens can zoom in or out to different focal lengths but it will maintain focus while moving. In addition, the camera can move to the left and right (pan) and up and down (tilt). PTZ stands for pan, tilt, and zoom.
Fixed
Position does not change
Varifocal
Focal Length can be changed, which decreases angle of view as it optically zooms in
PTZ
Can pan, tilt, and zoom (image shows a zoom in PTZ panning left and right)
When you should use a Fixed Lens Camera
- Because they are economical, fixed lens cameras are the workhorses of every surveillance system
- Use them to monitor all entrance points, both commercial and residential, and all corporate or public indoor and exterior spaces
When you should use a Varifocal Camera
- When you have a gate, door, or other known entrance point but can't mount a camera close by
- When you must get a close shot to identify a person or vehicle at distances greater than 50 feet, but less than 500 feet, and have a good idea where they are going to be (for example, people tend go through gates)
- Whenever you have an outdoor physical asset (ancillary building, designated fleet vehicle parking spots, oil pumping station, solar panel array, etc) with a fixed location
- Whenever you have a long, narrow area to watch, such as a hallway or warehouse aisle
When you should use a PTZ Camera
- Whenever you want to be able to manually change what the camera is looking at
- Whenever you must get a close shot to identify a person or vehicle at distances greater than 50 feet and you don't have a very clear idea where they are going to be
- Whenever you must get a close shot to identify a person or vehicle at distances greater than 500 feet
- Whenever you need to one of the 6 amazing things that you can do with SCW PTZ Cameras
Choosing the Right Body Style: Bullet, or Dome
IP cameras (other than PTZs) come with one of three body styles, and many people want to understand the Bullet Vs. Dome Camera question, but most of the time it comes down to personal preference.
- Bullet, mounts most easily on the wall, so usually used outdoors
- Dome, mounts most easily from the ceiling, so usually used indoors
- Turret, mounts most easily from the ceiling, so usually used indoors
Pros
Easiest to Install
More Obvious
Easy to Reposition
Can usually recognize people and license plates at greater distances
Better Night Vision, Less IR Bounce Back
Greater number of Long Range Camera Options
Cons
Camera Shape Can Support Spider Webs or Bird Nests
Pros
Hard for Vandals to Change Direction of Camera
Harder to see where the Camera is pointed
Usually has a wider field of view
Cons
Harder to Install
Harder to Reposition
Harder to Keep Glass Dome Clean
Glass attracts Dust and Fingerprints
More IR Bounce Back
More Discreet
Some People Forget to Tighten the Glass Dome and Moisture Gets In
Dome can Trap Condensation, Even When Properly Tightened
Can usually recognize people and license plates at shorter distances
Pros
Easier to Install than a Glass Dome
Won't Trap Condensation
No Glass Dome To Get Dirty or Dusty
No Glass Dome to Attract Fingerprints on
Better Night Vision, Less IR Bounce Back
Usually has a wider field of view
Cons
Camera Shape Less Likely than Bullet but Can Support Spider Webs
More Discreet
Can usually recognize people and license plates at shorter distances
Our IP Camera Selection
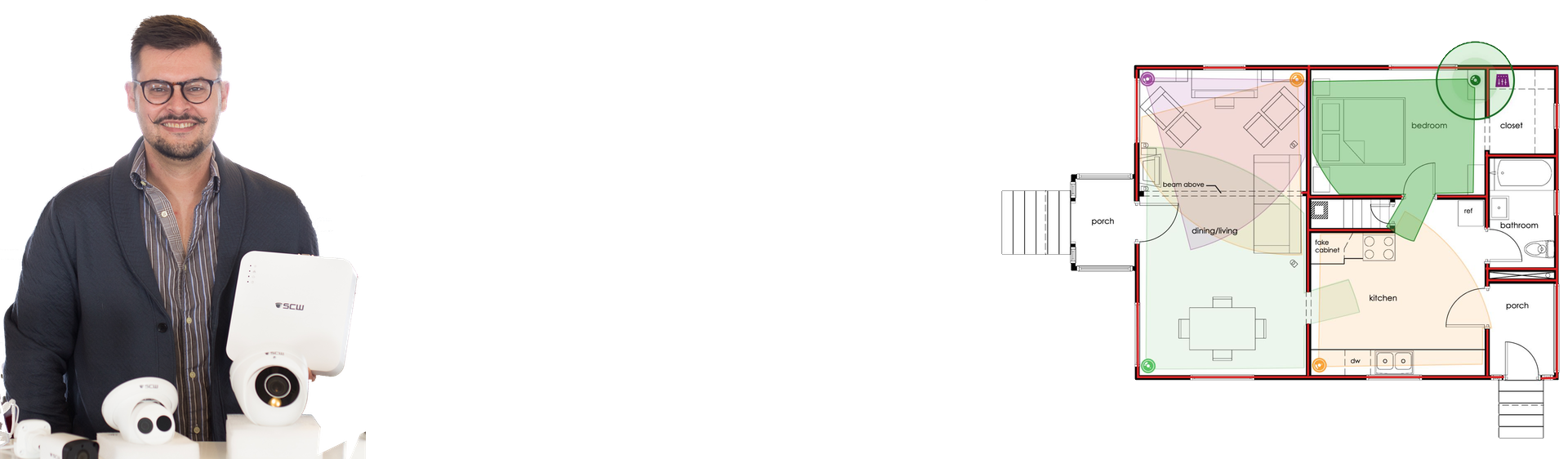
Lean on the experts
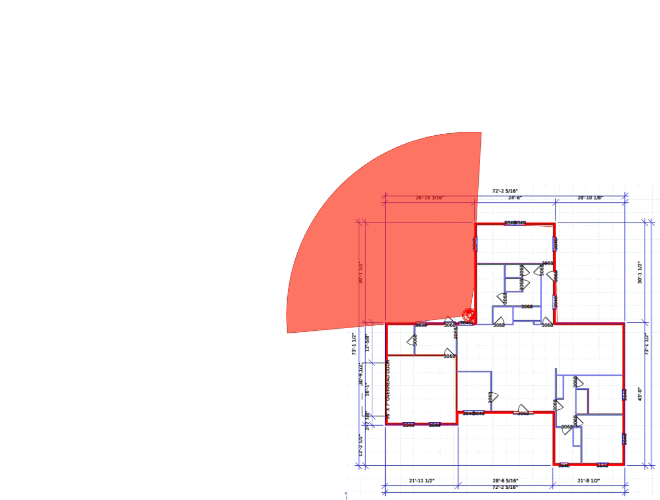
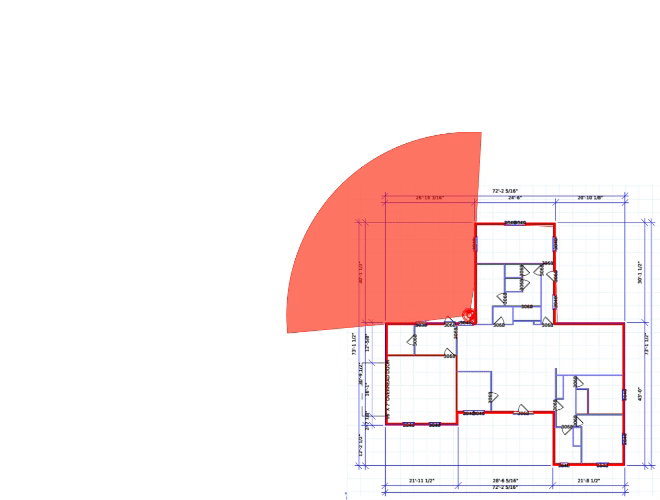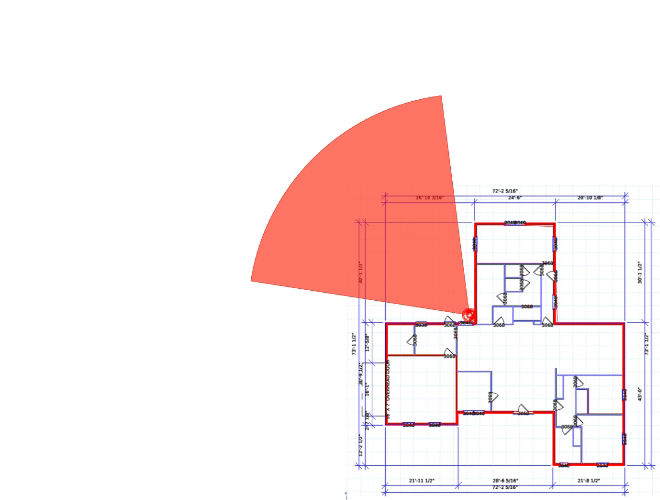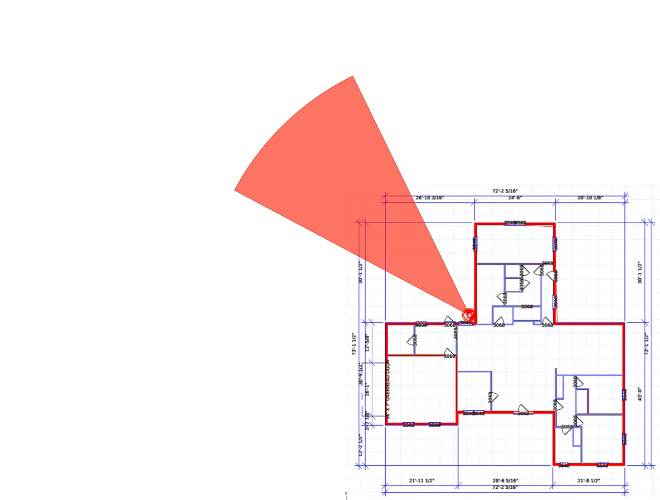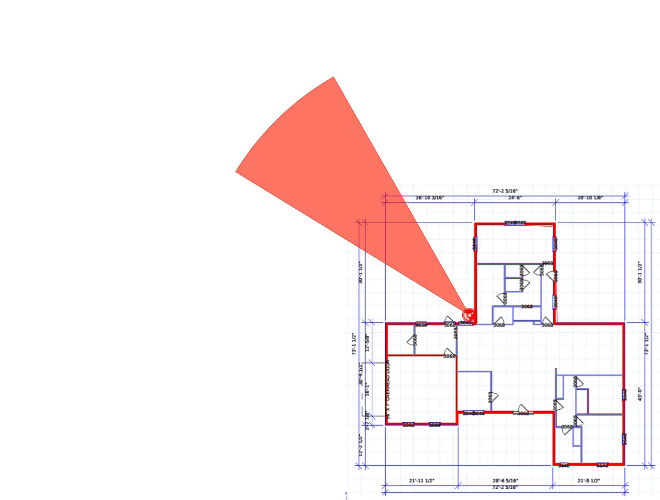
We'd be happy to work up a custom quote or take your floorplan and create a security coverage map.
Get aCustom Quote




































