With NVRs
Our NVRs are capable of recording in but allow you to set resolution and framerate
Available in or
channel configurations
All models have Schedule, Motion, Event, and 24/7 Recording Modes
Two Lines of NVRs: Admiral and Imperial
What's the main difference between the lines? Admiral has POE ports in 4, 8 and 16 port configurations. Because POE has a limit of around 900 feet, they are used on projects with smaller camera counts or shorter cable runs.
Imperial line use a dual or quad lan setup so that POE switches can be chained across a larger environment. Imperial line NVRs are available in 32, 64, 128, or 256 channel configurations.
The Admiral and Imperial Features
Smart Analytics Search
1 Click Firmware Update
Redundant NAS Backup
Event-Based Email Alerts
Remote Footage Download
H.265 Compression Store 40% More Footage
Three Recording Modes: Continuous, Motion, and Event
4K HDMI Outputs 1080P VGA Output
Remote Footage Download
Advanced Analytics: Motion Detection Line Crossing Intrusion Detection Face Detection Vandalism Detection
What is a Networked Video Recorder (NVR)?
Your NVR is the brain of your security system. It receives, processes, and stores the digital footage from your digital or IP cameras.
NVRs are servers that publish a webpage where you can view your cameras. They are embedded devices that you can connect to with desktop or mobile applications and then stream footage or watch recordings. They are analytics devices that check for someone or something crossing a line, entering or dwelling in an area. They are appliances that can display cameras on a monitor or multiple monitors.
NVRs are not DVRs
Often NVRs are mistakenly called DVRs, but they are different. A DVR is designed to process footage from analog cameras transmitting not yet digitized footage over outdated BNC cabling. Examples of analog camera technologies include AHD, CVI, TVI, and SDI. An NVR receives footage from digital or IP cameras transmitting data over an ethernet cable (Cat5, Cat6, or even Cat7). Analog systems are outdated and we do not recommend them anymore.
NVRs vs DVRs
NVRs are not DVRs
Often NVRs are mistakenly called DVRs, but they are different. A DVR is designed to process footage from analog cameras transmitting not yet digitized footage over outdated BNC cabling. Examples of analog camera technologies include AHD, CVI, TVI, and SDI. An NVR receives footage from digital or IP cameras transmitting data over an ethernet cable (Cat5, Cat6, or even Cat7). Analog systems are outdated and we do not recommend them anymore.
Helpful Guides
- Recording Time :: Hard Drive Calculator
- Motion Detection Features
- Commercial Grade Quality
- Automatic Backup Options
- ONVIF compliance
- Cyber Security for Physical Security
- How to setup Line Crossing (Tripwire)
- How to setup Intrusion Detection
- How to use Smart Search
- How to Setup People Counting
- How to Setup Camera Vandalism Detection
- How to Setup Audio Detection
Our NVR Selection
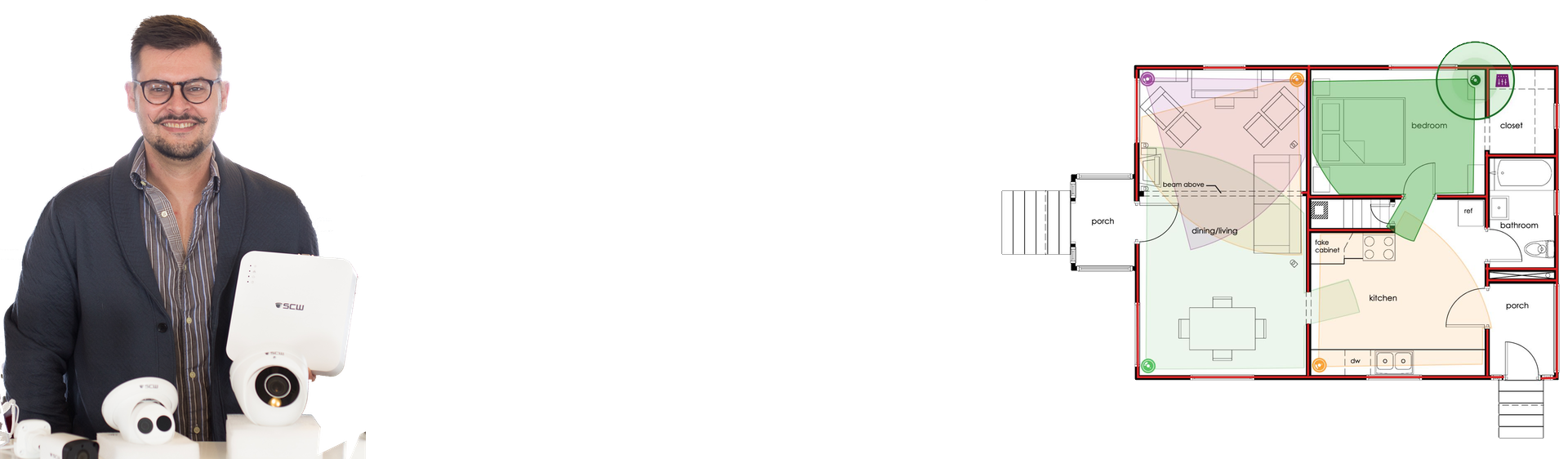
Lean on the experts
We'd be happy to work up a custom quote or take your floorplan and create a security coverage map.
Get aCustom Quote























